Featured
The Appalling State of Muslims in post-colonial India
Published
3 years agoon
By
Naira Mir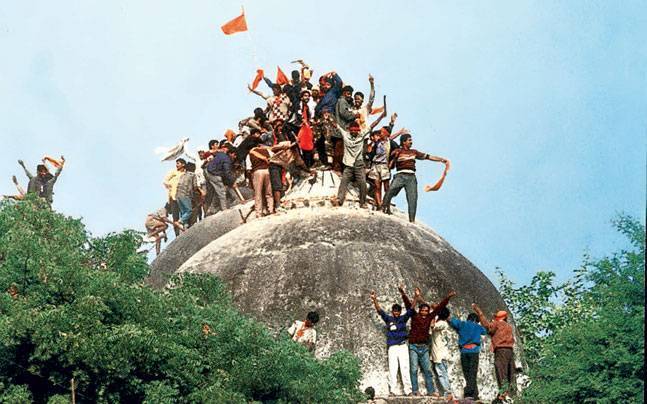
South Asia is home to one-third of the world’s Muslim population. Contrary to the popular belief there are more Muslims in South Asia than there are in middle-east which is popularly known to be the heart-land of Islam. After Indonesia, India is the second country in the world with the largest Muslim population. India is anciently known to be the hub of Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. So, when and how did a country largely consisting of Hindus, Buddhists and Jains become so densely populated by Muslims? How did Islam emerge in pre-colonial India? As much as there is a controversy around this inquisition, there is also a lack of historical, geographical and political awareness related to it. The most important aspect to this bone of contention is the appalling state of the Muslims in post-colonial India, and how is it different from that of the Muslim diasporas in the rest of the world, in specie the West. Albeit there have been events of religious violence in pre-colonial and British India, the post-colonial period has seen an enormous increase in riots and hate crimes against Muslims in India.
Also read, India Ranks 161st in Terms of Journalistic Freedom- RSF
The Image of Muslims in the West
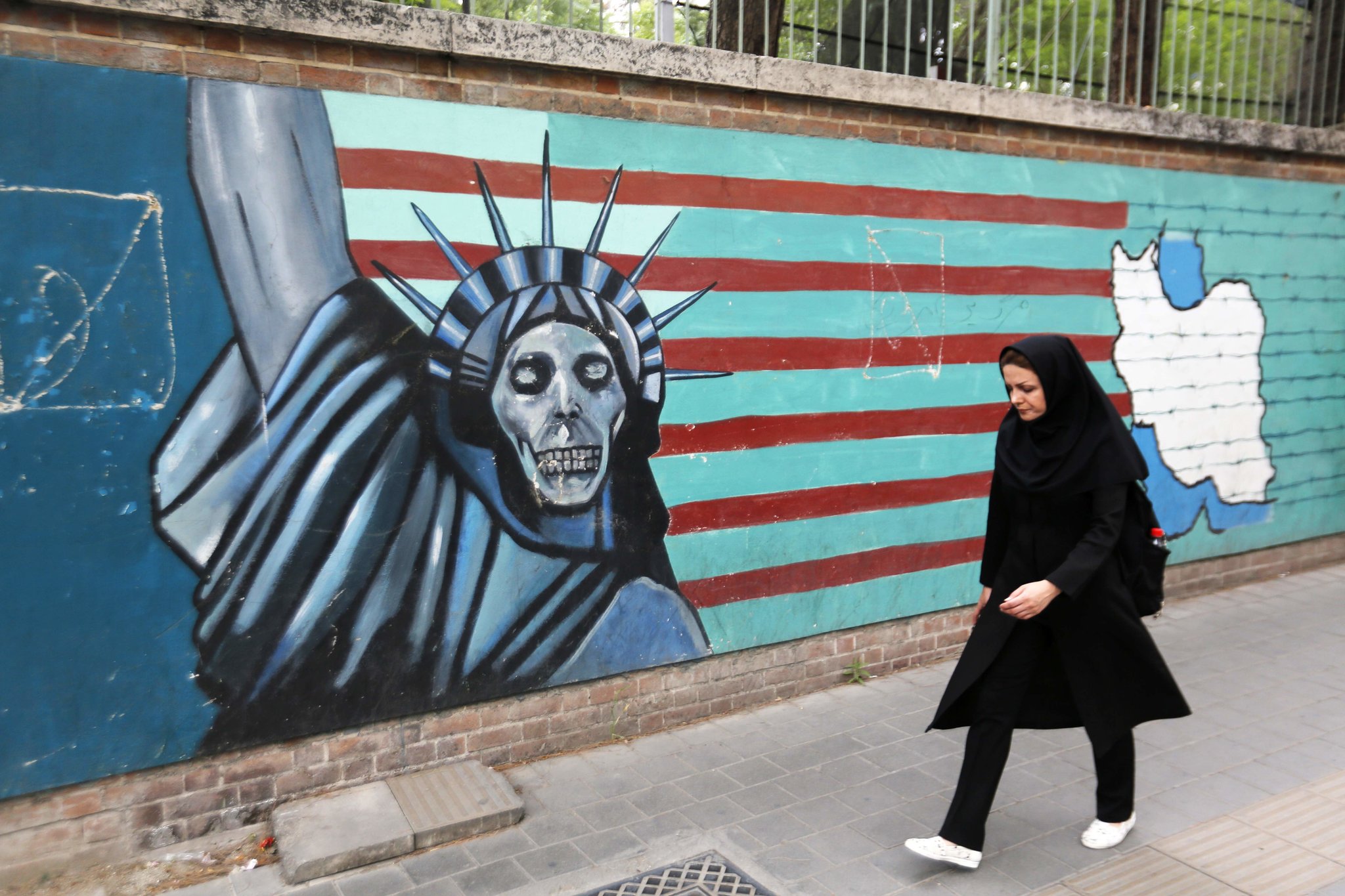
The image of Muslims in the west has been in question lately more than ever in the world in general. The rise of hate crimes against Muslims usually chalk up to the 9/11 attack against the United States which was allegedly carried out by a religious extremist organization Al-Qa’ida. Having said that there have been some crucial conspiracy theories that called for a new investigation into the attacks, because they asserted that there was evidence of individuals from within the US government being either responsible for or knowingly having conspired in the attacks as a means for America of justifying the war in Afghanistan and Iraq. However, majority of the general public held the opinion that Al-Qai’da had orchestrated the attack. Because the members of the Al-Qai’da were people who proclaimed to be the adherents of the religion of Islam, this gave rise to a sense of bigotry and intolerance in the west towards the entire Muslim community.
The widely accepted notion among the broad commonality incriminated the Muslims of effectuating the attack. Non-Muslims started generalizing Muslims and started viewing them as people who endorsed terrorism, which led to a common prejudice against them in the western society. From their customs and religious practices, including their eating habits, to their appearance and clothing, Muslim men and Women were looked down upon and stereotyped as radical and fundamentalists. This generalization and stereotyping of Muslims gradually turned violent in nature and this turn of events gave rise to a series of hate crimes resulting in abuse and even unfortunate deaths of many Muslims. Howbeit, even before the 9/11 attack, many bookmen and laypeople alike had accepted a prior perception that religious terrorism had become the most common form of terrorism, particularly with regard to Islam. This suggests that Islamophobia was a common practice even before 2001.
Read here, “The Kerela Story” Controversy in India
Islamophobia before 9/11
People have associated Islamophobia with various manifestations. While some people reckon the phenomena with the increasing population of Muslims in the United States and Europe, others deem it to be retaliation for an ostensible anticipation of the emergence of a global Muslim identity. Yet many others identify Islamophobia with xenophobia and racism. Another less talked about reason for Islamophobia is the media’s double standards while reporting terrorism. A recent study has found out that terror attacks by “muslims” receive 357% more press attention. This was University of Alabama researcher’s newly study which was published in Justice Quarterly (academic journal covering criminology and criminal justice) authored by Dr. Erin Kearns, UA assistant professor of criminology and criminal justice. Still and all the causes of Islamophobia have always been and till date are debatable.
In the spate of attacks on Muslims in the western countries including the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Switzerland and New Zealand, it should be noted that the occurrence of such deplorable crimes in the West have one regularity. They are all driven by Islamophobia, the impetus of which is the bigotry for Muslims, a sequence to the specious notion that Muslims endorse Terrorism.
Also, read Muslim OBC Reservation scrapped by BJP government of Karnataka
Appalling State of Muslims in post-colonial India- Partition
Talking about Islam and Muslims, then like in West the appalling state of Muslims is much the same in parts of South Asia explicitly in India, but for wholly different reasons. Though there have been incidents of religious violence in pre-colonial and British India, the history of modern India has seen a compelling surge in the estimate of both subjective and objective violence. But what accounts for this rise of violence against Muslims in independent India? Is it Islamophobia that drives this hatred, just like it does in the West.
Inasmuch these crimes are a result of anti-Muslim sentiments in both the West and in India, the causes of these crimes are primitively much different. Benchmarking the nature of these crimes and the disparity in the claims of the perpetrators, one finds out that there is significantly a historical aspect to the nature of violence against Muslims in India. The partition of British India into two different countries, now called India and Pakistan, was originally borne out of a religious divide amongst Hindus and Muslims. As history claims, different people were for and against partition, as each had a different vision in mind.
There are many theories that explain the reasons for the establishment of Pakistan. One of the most agreed upon consensus of the pro-partition leaders for the formation of Pakistan was the subject of safety of the Muslim minority in the otherwise Hindu majority India. The earlier incidents of religious violence in India had taken a toll on both the Hindus and Muslims. The Muslims being the minority were now more insecure about their safety while living amongst Hindus. Because the safety of Muslims had been in question, ultimately the demand for a separate country for Muslims by the pro-partition leaders was unanimously supported by most Muslims. The Muslims who were not able to migrate then to the land given to Pakistan were left in India, and thus were even less in number, making them an even smaller minority than before.
Read here, India- The Killing of Gangster-Turned-Politician Atiq Ahmad
Commencement of the Appalling State of Muslims in post-colonial India
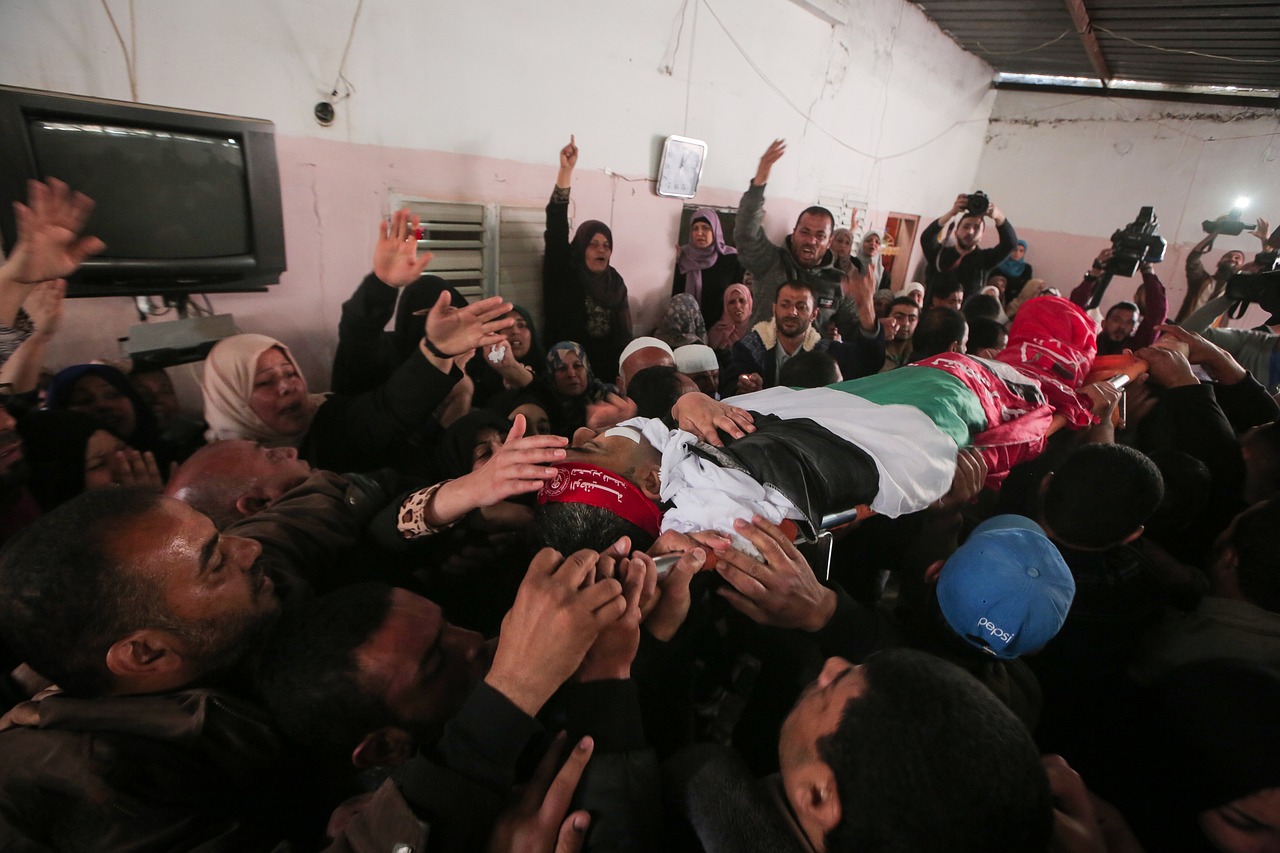
What marked the commencement of the violence against Muslims in Independent India was the demolition of Babri Masjid, a 430 year old mosque in Ayodhya by extremist Hindus and members of Vishwa Hindu Parishad(VHP) and Bajrang Dal. What followed was a sequel of incidents feuled by the religious animosity stirred between Hindus and Muslims. There has been a continuing rise in the manifestation of hate crimes and incidents of religious prejudice against Muslims in India ever since. However, with the emergence of the current government in India, the last few years have seen an enormous and noticeable amount of hate driven crimes including rape, public flogging and lynching. The motives of the perpetrators for committing such heinous crimes are as bizarre as they are abominable. Concepts like cow vigilantism and theories like “Ghar Wapsi” have been doing rounds in the air and have accounted for most of these crimes if not all.
Also, read UN Defender Demands End to Crackdown on Kashmiri Activists
The idea of “Ghar Wapsi” in the appalling state of Muslims in post-colonial India
The idea of “Ghar Wapsi” has also been endorsed and publicized by the right-wing extremists in India, including the leaders of the current government. It is a concept that propagates religious conservation of non-hindus to Hinduism. The reason behind the ideology of these people is their belief that all the people living in pre-colonial and ancient India were originally Hindus. They believe that the emergence and presence of non-hindus in India is only because of the forced conversions by missionaries and invaders that came to India from outside, who were by and large Muslims. This ideology is linked to the pre-colonial past of India. It refers to the period when Islam first emerged in India in 711, when Mohammad Bin Qasim, who was a general in the Umayyad -empire conquered the area of the Southern Pakistan. This was the initial interaction of Islam with South Asia.
Afterwards in the 13th century, the Mongol Invasion uprooted a large number of Persian Turks from Iran and Central-Asia driving them to India where they settled in. And so gradually the tradition and practices of these people started to blend in the syncretic culture of India. Subsequently in the late 13th century with the establishment of the Empire of Timur, began the era of the rise Muslim rulers in India.
Later on in 1526, Babur, a direct descendant of Timur, founded the Mughal Empire, which then ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent for more than 200 years. During the growth of the Mughal Empire under Babar’s son Akbar (1526-1605) there was an essential blending of Hindu-Muslim cultures. Akbar married a Hindu princess of a pure Hindu Rajput blood-line. This made Akbar’s son Jehangir half Rajput and half-Hindu. After Akbar, his son also married a Hindu woman, and therefore Jehangir’s son Shahjahan was three-quarters Rajput. With the rise of the Mughal Empire, biologically each successor of the dynasty became less and less Turkic and more and more Indian. They adapted the culture of India and also the Indian culture was insinuated by the Islamic traditions, resulting in the concoction of two separate cultures and religions.
Read here, Festival turns bloody after Hindutva Mob Burnt Centennial Mosque
Historic Bias as a reason for the Appalling State of Muslims in Post-Colonial India
These religious and cultural adaptations are, however, still seen as unethical and blameworthy by many Hindus in India, as they see Islam as a threat to their own culture and identity, as a foreign concept brought to India from outside. They consider the presence of Muslims in India as a result of the historic invasions and forceful conversions by Muslim outlanders and conquerors, and not the gradual amalgamation of two different cultures and religions over the course of time. Crimes like lunching and theories like “ghar wapsi” are not mere co-incidents but are borne out of such historic beliefs. They are a corollary of a historic hurt that these people carry. The violence in the west or bread out of islamophobia is sporadic in nature and often spontaneous while in India violence is structured. Unlike the west, the primeval and ever-growing intolerance towards the practices and culture of Muslims in modern day India is not because of the nature of these practices. On the contrary, in India Islam as a religion is not seen as much of a threat but Muslims are.
Also, read Dehumanizing Representation of Tribals and Muslims in the Oscar fame RRR
You may like
-


The War No One Sees: What Will it Take to End Gaza’s Humanitarian Crisis
-


Muslims have more reasons to hate the US than the other way around
-


Muhammed: The Greatest Man to walk on Earth
-


India: Rise in Police Encounters in UP Under Yogi Adityanath’s Leadership
-


Manipur Violence Sparks Debate in Indian Parliament
-


Communal Clashes in Haryana: Gurugram Mosque Set Ablaze, Four Killed in Nuh
Featured
Board of Peace Explained: New Global Peace Architecture or Another Power Play?
Published
5 days agoon
January 19, 2026
This is not just about a region in this world where human rights are not given, and people are being killed. It is about humanity, life, and the very foundations of values that humans are living with. When Gaza is discussed today, it is rarely in the language of rights. It is discussed as a problem to be solved, a territory to be stabilized, and a population to be administered.
The announcement of a new international “Board of Peace” fits neatly into this pattern. Presented as a bold initiative to guide Gaza out of conflict and into reconstruction, the Board of Peace has been framed by its sponsors as innovative, inclusive, and forward-looking. Yet for Palestinians, the announcement raises an older, still unresolved question: Who decides Gaza’s future, and on what authority?
What Is the Board of Peace?
The Board of Peace was announced by US President Donald Trump as part of a broader Phase Two Gaza plan, marking a shift from ceasefire management to post-genocide governance and reconstruction.
According to official descriptions, the board is meant to:
- Oversee Gaza’s political transition
- Coordinate reconstruction funding and investment
- Provide international supervision during a “transitional” period
Trump declared himself chair of the board and described it as a high-level body composed of political leaders, financial figures, and diplomatic actors. Unlike the United Nations, the board has no clear treaty basis, no General Assembly mandate, and no defined accountability mechanism.
It is powerful not because it is formal, but because it is backed by money, political leverage, and security control.
Who is on the Board?
The individuals named or referenced in connection with the Board of Peace are not neutral facilitators.
The board’s executive circle includes:
- Marco Rubio, US Senator and the Secretary of State
- Tony Blair, former UK prime minister
- Jared Kushner, Trump’s son-in-law and former Middle East envoy
- Steve Witkoff, US real estate magnate and political donor
- Ajay Banga, President of the World Bank
These are figures associated with Western political power, financial institutions, and security-centric diplomacy. None are elected Palestinian representatives. None comes from Gaza. The imbalance is structural, not incidental.
Which Countries Were Invited?
One of the board’s defining features is its attempt to project global legitimacy through invited state participation.
According to credible sources, Trump sent invitations to around 60 world leaders. Those explicitly named in reporting include:
- Turkey (President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan)
- Egypt (President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi)
- Canada (Prime Minister Mark Carney)
- Argentina (President Javier Milei)
Moreover, some diplomatic sources also indicate the list includes:
- Britain
- Germany
- Italy
- Morocco
- Indonesia
- Australia
The Palestinian Face of the Plan: Who Is Ali Shaath?
To provide the plan with Palestinian leadership, the US has backed Ali Shaath as head of the transitional Palestinian committee that will administer Gaza’s civil affairs under the Board of Peace.
Shaath’s profile is central to understanding how this governance model is being sold.
Here is a quick overview of Ali Shaath:
- He was born in 1958 in Khan Younis
- He is a civil engineer with a PhD from Queen’s University Belfast
- He previously served as deputy minister of planning in the Palestinian Authority
- He has worked on industrial zone projects in both Gaza and the West Bank
Shaath has spoken publicly about the scale of Gaza’s destruction, estimating around 68 million tons of rubble, much of it contaminated with unexploded ordnance. He has suggested that clearing debris could take three years, with full recovery achievable in seven years. It seems to be a far more optimistic timeline than UN estimates, which warn that rebuilding could extend beyond 2040.
Politically, Shaath has been described as acceptable to both Hamas and Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas, precisely because he is positioned as a technocrat rather than a political leader. However, it is yet to be observed how he would work with the other members.
Governance Without Sovereignty
The Palestinian committee, chaired by Shaath, has issued a mission statement pledging to restore services, rebuild infrastructure, and stabilize daily life in Gaza.
The committee describes its work as “rooted in peace” and focused on technocratic administration rather than politics.
Yet the committee:
- Controls no borders
- Commands no security forces
- Regulates no airspace or coastline
- Has no electoral mandate
It governs without power, while power remains in external hands.
When it comes to the reaction of the people of Gaza, they showed mixed feelings of skepticism over hope. Some Palestinians express cautious hope that any plan might bring electricity, water, and an end to constant displacement. Others see the Board of Peace as another externally designed structure that manages Gaza without addressing the occupation.
Peace Architecture or Power Management?
The Board of Peace is being presented as an innovation. However, history offers a cautionary lens.
Temporary governance structures in occupied or post-conflict territories have a habit of becoming permanent. Reconstruction becomes conditional. Aid becomes leverage. Administration replaces self-determination.
In a nutshell, the Board of Peace asks the world to believe that stability can precede justice, and that governance can substitute for freedom.
For Palestinians, the unanswered question is simpler and older:
If Gaza’s future is designed in Washington, financed in global capitals, and overseen by external boards—where does Palestinian self-determination actually begin?
Until that question is addressed, the Board of Peace risks becoming not a new architecture for peace, but another structure built on the same imbalance that has kept Gaza unfree for decades.
Peace cannot be outsourced, and a people cannot be rebuilt while being brutally ruled.
Featured
Phase Two of Gaza’s Plan: Demilitarization, Technocracy, and a Ceasefire That Still Bleeds
Published
5 days agoon
January 19, 2026
The second phase of Gaza’s so-called peace plan has officially been announced. It is being described as a transition from ceasefire to governance, from violence to rebuilding. However, on the ground in Gaza, the distinction is harder to locate.
Isn’t it shocking that more than three months after the ceasefire took effect in October, Palestinians are still being killed, and aid is a privilege to have? Entire neighborhoods remain uninhabitable. So, the announcement of phase two does not coincide with calm. It arrives amid continued military pressure, delayed withdrawals, and a humanitarian system operating far below what was promised.
There is a crucial question Palestinians are asking, and that is not whether Phase Two exists on paper, but whether it alters the reality of power.
What Phase Two Claims to Change
According to some US officials, Phase Two is meant to shift the Gaza file from emergency truce management to long-term stabilization. Its three pillars are clear:
- First, the demilitarization of Hamas and other armed groups, framed as a non-negotiable precondition for any durable peace.
- Second, the establishment of a Palestinian technocratic committee to administer Gaza’s civil affairs during a transitional period.
- Third, the beginning of reconstruction planning, coordinated under international supervision and tied to security compliance.
In theory, this is where genocide ends, and governance begins, but in practice, each pillar raises more questions than answers.
Phase One by the Numbers: A Ceasefire in Name
Before moving further, let’s have a look at the overview of Phase One. Since the ceasefire came into force on October 10, at least 451 Palestinians have been killed and more than 1,250 injured, an average of nearly five deaths per day. Military operations continued under the language of “enforcement” and “targeted action,” blurring the very meaning of a ceasefire.
When it comes to the prisoner exchanges, Hamas and Israel both released most of the captives. Bodies were also exchanged, with one reportedly still trapped under rubble.
Aid delivery fell far short of commitments. Between October and early January, around 23,019 aid trucks entered Gaza out of a promised 54,000, roughly 43% of the target.
Critical crossings, including Rafah, remained closed or heavily restricted. Aid organizations reported operational paralysis as bans, inspections, and suspensions multiplied.
In other words, Phase One did not fulfill its promises. It managed the violence without ending it.
Demilitarization Before Relief
Phase Two places demilitarization at its core. President Trump has repeatedly framed it as a binary choice—an “easy way or a hard way.” The message is unambiguous: disarmament first, normalization later.
What remains unaddressed is the imbalance this creates. Israel retains control over Gaza’s airspace, coastline, borders, population registry, and imports. Palestinian armed groups are asked to disarm while occupation-level controls persist.
It is pertinent to mention that international law does not recognize demilitarization as a substitute for political rights. Yet phase two calls itself the engine of peace, while humanitarian access, withdrawal timelines, and accountability for genocidal destruction remain secondary.
For many Palestinians, this sequencing feels less like peacebuilding and more like containment.
The Technocratic Committee: Governance Without Power
There will be a 15-member Palestinian committee tasked with administering Gaza’s civil affairs. Its stated mission includes restoring basic services, managing reconstruction, and laying foundations for stability.
Its members are presented as non-political professionals, including engineers, administrators, and planners. But what is missing is authority.
The committee operates under external oversight, with no electoral mandate, no independent security control, and no ability to regulate borders, trade, or movement. Its legitimacy is managerial, not democratic.
However, it’s not shocking for Palestinians as they are familiar with this model. Over the past three decades, “temporary” arrangements have repeatedly substituted administration for sovereignty. Technocracy becomes a way to manage populations without resolving the structures that disempower them.
Palestinian Voices
Some reports from Gaza capture a mood that is neither celebratory nor dismissive, but only exhausted.
Some residents express cautious hope that Phase Two might at least bring predictability: electricity that lasts more than a few hours, water that runs clean, streets cleared of rubble. On the other hand, most of them see another externally designed plan that speaks the language of peace while preserving the architecture of control.
One displaced man described being forced to move 17 times since the genocide began. Another questioned how demilitarization could be discussed while entire families still sleep in tents beside the ruins of their homes.
For many, peace is not an abstract framework, but the ability to survive the night without fear.
Aid as Leverage, Reconstruction as Reward
Phase Two introduces reconstruction, but not as a right. Aid and rebuilding are explicitly linked to compliance. This conditionality transforms humanitarian relief into a pressure tool.
History offers little comfort here. Millions pledged to Gaza after previous acts were delayed, diverted, or blocked entirely. The difference now is scale. Gaza’s destruction is unprecedented, with tens of millions of tons of rubble, unexploded ordnance, and erased neighborhoods.
Therefore, rebuilding without political change risks entrenching dependency rather than restoring dignity.
A Governance Phase Built on Unresolved Violence
Although phase two is described as a transition, transitions require movement—away from violence, toward rights.
So far, what has changed is not the structure of power, but the language used to describe it.
Demilitarization is demanded without de-occupation. Governance is promised without sovereignty. Reconstruction is discussed while restrictions remain.
This is not peace delayed. It is peace redefined—away from justice, toward management. Ultimately, nothing can substitute for Gaza’s right to determine its own future, which has been denied for decades.

When governments talk about protecting children, their words rarely match what young Palestinians are living through. In the Gaza Strip, education is not merely disrupted; it is being systematically erased, leaving the possibility of a generation without basic schooling and awareness.
A recent analysis done by the University of California warned that children in Gaza may lose the equivalent of five years of education due to repeated school closures since 2020. These conditions are compounded by violence, trauma, and chronic destruction of infrastructure.
Almost all of the schools have been partially or completely destroyed by Israel. If schools remain out of session until at least 2027, many teenagers will be a decade behind where they should be educationally.
This is not only about education but the erasure of an entire generation, coupled with despair. It is ultimately the humanitarian consequence of genocide-scale violence and blockade. The future is being stolen from innocent lives, and the world is witnessing one of the greatest catastrophes in the history of mankind.
The Scale of the Education Collapse in Gaza
Before the genocide intensified, Gaza had an education system serving nearly 660,000 school-aged children. However, two years of bombardment, destruction, and blockade have devastated this system:
- An estimated 97% of schools in Gaza are damaged or destroyed.
- Hundreds of thousands of children have had little to no access to face-to-face schooling for more than two academic years.
- More than 18,000 students and 780 teachers were killed as of October 2025, according to UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) data included in international analysis, representing a massive depletion of both students and educators.
- UNRWA reported that around 660,000 children are out of school, with many classrooms repurposed as shelters for displaced families.
These figures combine lost school buildings with lost lives and lost opportunities. These conditions are creating structural barriers to learning that go far beyond temporary closures.
What It Means to Lose Years of Education
According to the Cambridge analysis, repeated closures since 2020, first due to the pandemic and then to ongoing genocide, have eroded more years of learning than children can realistically recover.
This isn’t just falling behind, but a fundamental derailment of life trajectory:
- Delayed literacy and numeracy milestones
- Increased likelihood of dropout in teenage years
- Higher risks of early marriage and child labor
- Limited access to higher education and careers
Resultantly, when education stops, social mobility also stops with it.
Education as a Protective Space
Children’s access to education is not just about reading and math, but about safety, structure, and psychological stability.
UNICEF and other child protection agencies have emphasized that education provides:
- Protection from exploitation and abuse
- Psychosocial support
- A routine that counteracts trauma
- Opportunities for social interaction and identity building
When schools are reduced to rubble or become temporary shelters, these protective functions disappear. Instead, Gaza’s schools increasingly resemble sites of trauma, displacement, and interruption, not growth.
Trauma, Hunger, and Learning Loss: A Spiral of Harm
The education crisis in Gaza does not exist in isolation, but it intersects with:
- Widespread hunger and malnutrition, which impair cognitive development
- Psychological trauma, which reduces concentration and memory
- Displacement and instability, which make regular attendance impossible
A recent scientific analysis describes how children exposed to conflict, displacement, and trauma face long-term developmental challenges, including reduced educational outcomes.
Comparing Gaza to Global Conflict Patterns
Gaza’s education collapse is one of the most extreme examples today, but it reflects a broader global trend.
UNICEF estimates that globally, more than 25 million children of primary age are out of school due to conflict and insecurity.
In wider conflict zones, from Yemen to Sudan, attacks on schools and displacement keep millions from education.
However, Gaza’s situation is exceptional for the scale of destruction, cumulative closure, and overlap with famine, displacement, and repeated bombardment.
The Lost Generation is Not Just a Phrase but a Forecast
Researchers warn that, unless things change, Gaza’s children will not simply “catch up.” They will represent a generation with permanent educational loss, with consequences echoing for decades.
This is the core of the Cambridge study’s warning:
“Children in Gaza will have lost the equivalent of five years’ worth of education… and many will be a full decade behind their educational level.”
Even temporary or online learning measures introduced by UNRWA and the Palestinian Ministry of Education have been severely constrained by destroyed infrastructure, scarce resources, and ongoing insecurity.
Why This Matters Beyond Gaza
When an entire generation loses access to education:
- Entire economies lose future professionals
- Communities lose rebuilding capacity
- Political stability becomes harder to achieve
- Human rights, including dignity and autonomy, are undermined
Gaza’s children are not only Palestinian future workers and citizens. They are part of the global Muslim community, and their loss echoes in every society that values human potential.
Their right to education is universal, and its denial is not a local tragedy but a global failure.
Trending
-

 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years agoWorld passively watching as Israel perpetrates open-ended massacre in Gaza
-

 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years agoArgentina wins the World Cup; are there any other winners?
-

 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years agoIsrael is Hiding Crucial Demographic Facts About Palestinians
-

 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years agoHistory of the Ottoman Empire
-

 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years agoChristian militia infiltrate Lebanon
-

 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years ago“Do Not Waste Water Even If You Were at a Running Stream” Prophet Muhammad
-

 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years agoMuhammed: The Greatest Man to walk on Earth
-

 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years agoWorld Leaders Remain Silent Over Human Rights Violations in the UAE