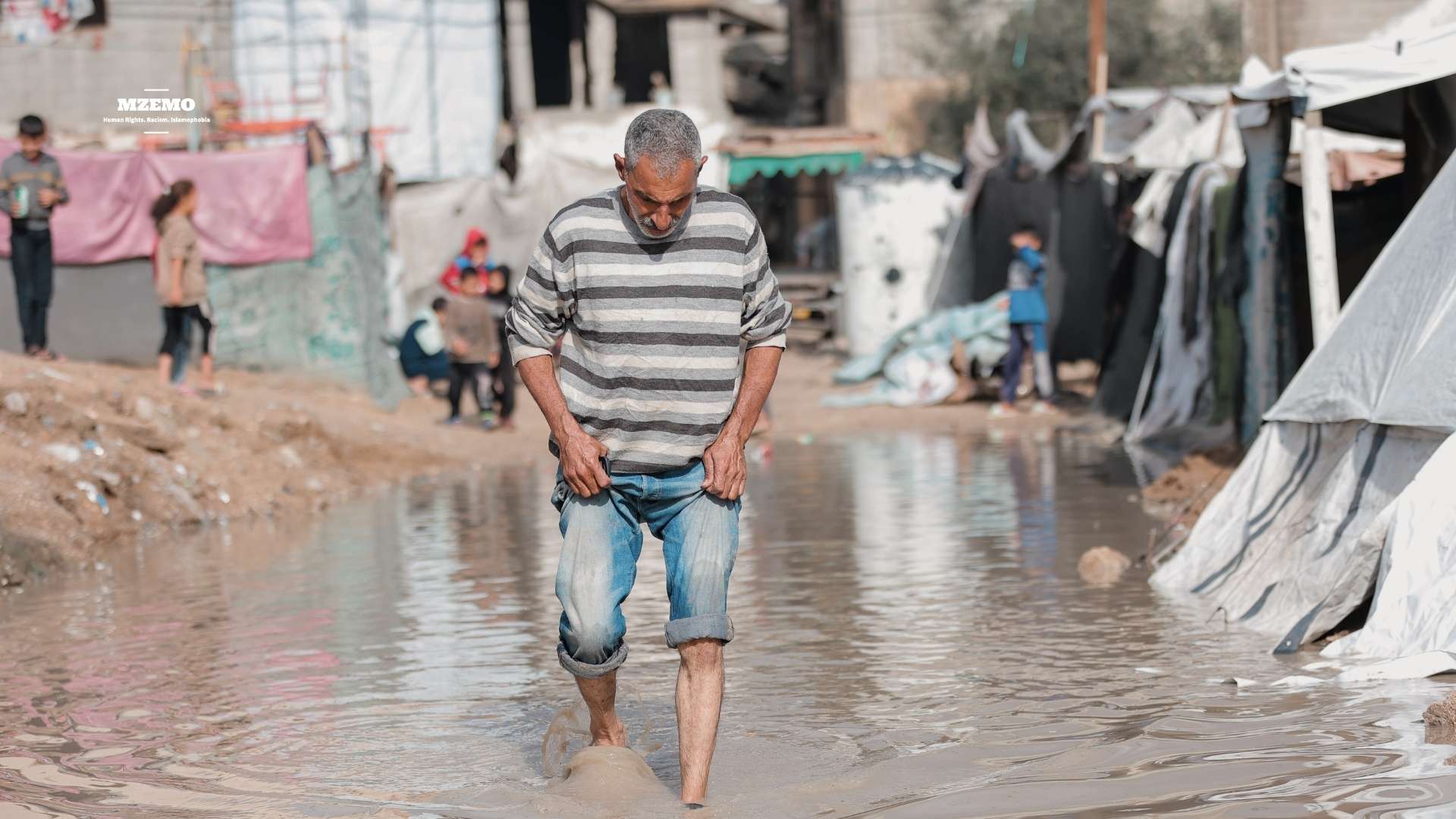
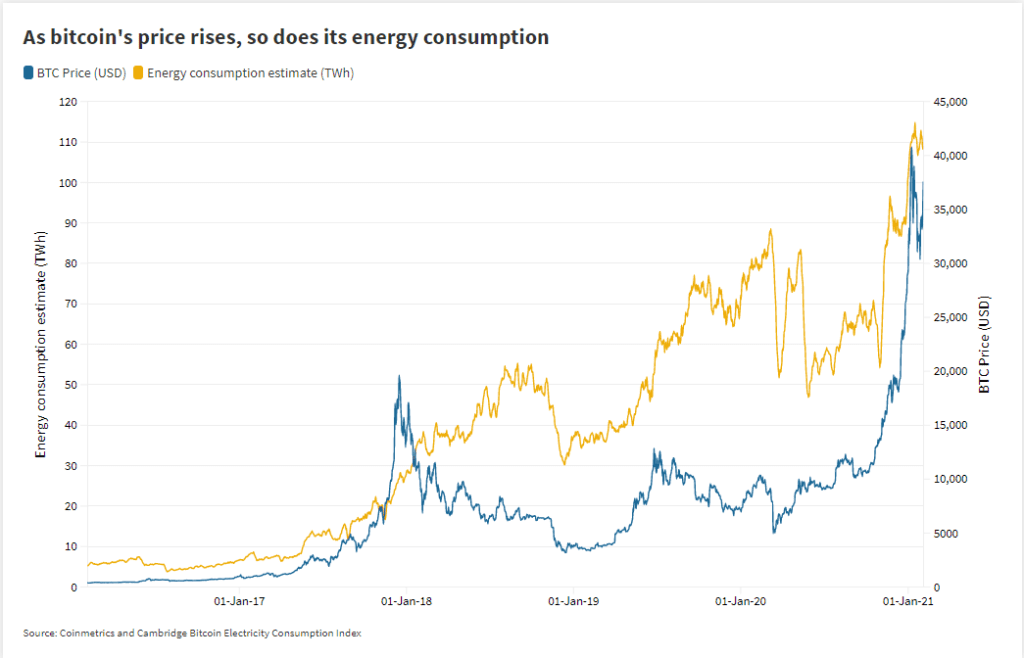Before sunrise, the camp is already awake. A woman steps carefully between puddles that did not exist the night before. To add more to the inhumane conditions, rainwater has mixed with waste and ash, turning the ground into a thin, foul-smelling slurry. She is carrying two empty containers, hoping the water point has not run dry again today.
Nearby, a child coughs, a persistent dry cough that has become common in the tents since winter set in. This is just a glimpse of life now for hundreds of Palestinians in Gaza. This is not a story of a temporary stop, nor of an emergency night or two, but of a prolonged existence inside fabric shelters that were never meant to last months.
According to the United Nations, around 1.7 million people remain displaced across Gaza. Not only that, a large share of them is living in tents, plastic shelters, or overcrowded informal sites. These sites are often pitched on rubble, farmland, or roadsides. The ceasefire might have changed the tempo of the war but for those in the camps, it did not restore normal life at all.
From Homes to Tents
Entire neighborhoods across Gaza have been flattened or rendered uninhabitable. As per the UN satellite assessments, well over half of Gaza’s housing stock has been damaged or completely destroyed, leaving families with no realistic option to return.
Tents were supposed to be temporary, but as the atrocities continue to inflict the people of Gaza, now these are standing for months.
Moreover, most of those tents offer no insulation. At night, cold air moves freely through torn seams. During rain, water pools inside, soaking thin mattresses and blankets. When storms hit, some tents collapse entirely, forcing families to crowd into neighboring shelters or even sleep outdoors until replacements arrive — if they arrive at all.
These are not the conditions for life to even exist. Aid agencies describe these sites less as camps and more as open-air holding zones, where survival depends on irregular deliveries of water, food, and fuel.
Smoke, Plastic, and the Air People Breathe
With fuel scarce and electricity almost nonexistent, many families burn whatever they can find to keep warm or cook food. Plastic packaging, scraps of rubber, and mixed waste are common substitutes.
The smoke hangs low in the evenings. Burning plastic releases toxic fumes that aggravate respiratory problems, especially among children and older people. A few clinics, which are fortunately left, operating inside or near displacement sites report rising cases of persistent coughs, chest infections, and eye irritation, conditions that are difficult to treat in overcrowded settings with limited medicine.
For many families, the choice is brutal. Either to breathe toxic smoke or to endure freezing nights. This is like a Hobson’s choice for them to live in these conditions.
Childhood on Hold
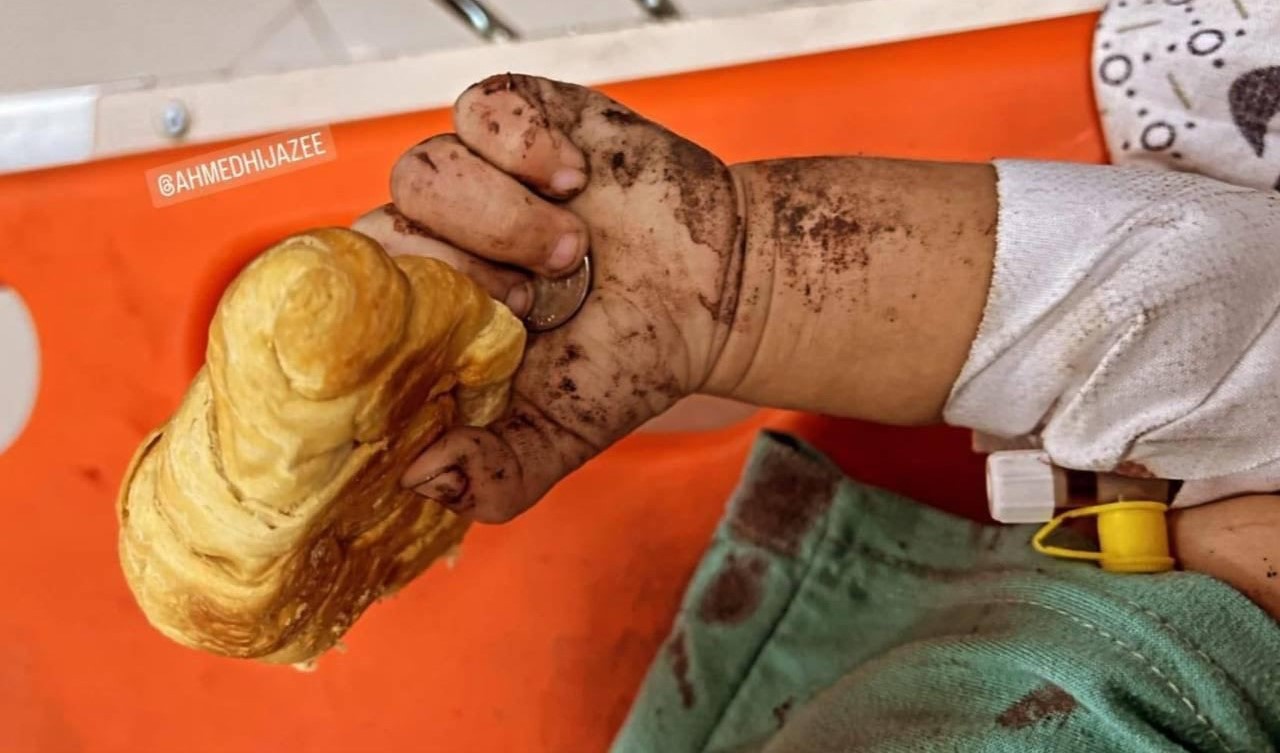
Children make up nearly half of Gaza’s population, and many are growing up almost entirely inside tents.
There is no school routine, no playground, and no sense of safety after dark. Parents describe children waking at night from cold, fear, or hunger. It is not surprising that the aid workers are noting signs of trauma, including withdrawal, bed-wetting, sudden aggression, and silence.
Mental health professionals working with humanitarian teams have warned that prolonged displacement, especially under such harsh conditions, can leave long-term psychological scars. On the other hand, counselling services are scarce, and survival needs usually come first.
For many children, days pass without structure. Time is measured not by lessons or play, but by queues for water, food distributions, and the arrival, or absence, of aid trucks.
Rain, Sewage, and the Winter Toll
The appalling living conditions were already very severe, but in the winter, it makes them tenfold, turning shelters into hazards.
Heavy rainfall has flooded multiple displacement sites, washing sewage into living areas and soaking tents beyond repair. In some camps, families have raised bedding on bricks or broken furniture in an attempt to stay dry.
Humanitarian reports, including those from Transparency International, document tents collapsing under wind and rain, forcing repeated displacement even within camps. Each move strips families of what little stability they have managed to create.
Cold weather has compounded illness. Without proper clothing, heating, or medical care, respiratory infections have become harder to manage. Clinics, already overstretched, struggle to cope with demand.
A Ceasefire Without a Way Home
For people living in tents, the ceasefire did not bring clarity. Some families hoped it would mean a return home. Instead, many areas remain inaccessible, unsafe, or destroyed. In some cases, new evacuation orders have continued, forcing further movement even after the fighting slowed.
Aid workers say uncertainty is one of the heaviest burdens. Families do not know whether to rebuild makeshift shelters, prepare to move again, or wait for instructions that may never come.
“We Are Still Here”
In the camps, people talk less about politics and more about endurance and survival.
They talk about missing ordinary things, like doors that lock, floors that are dry, and nights without smoke. They talk about children growing up too fast, about illness that lingers, about days that blend into each other.
One displaced man summed it up simply: “We are alive, but this is not living.”
In a nutshell, survival continues, measured in blankets, liters of water, and the hope that tomorrow will bring something other than uncertainty to breathe.


 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago
 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago
 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years ago
 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured4 years ago
Featured4 years ago
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Bitcoin_Mining_Work_Dec_2020-01-bd91c1773e5d4320b9b0e3cee1ecc4fd.jpg)