The Mediterranean dawn on 2nd October, 2025, was meant to carry a different story. For hundreds of activists aboard the Global Sumud Flotilla, including doctors, artists, parliamentarians, and volunteers from over 37 countries, it was a mission of a lifetime. Their ships carried medical supplies, food packets, and a message written in humanity’s oldest language: solidarity. However, as Israeli naval vessels surrounded them 40 nautical miles from the Gaza Strip, that message was silenced most brutally. Within hours, the flotilla had been seized, its passengers zip-tied and blindfolded, and its aid confiscated.
Israel’s interception of the Global Sumud Flotilla is not just a naval incident but another chapter in the long story of Gaza’s suffocation. In a land already starved by siege, famine, and bombardment, this act tightened the blockade around two million civilians who had endured what human rights organizations now recognize as a continuing genocide.
Gaza in Famine: A Manufactured Catastrophe
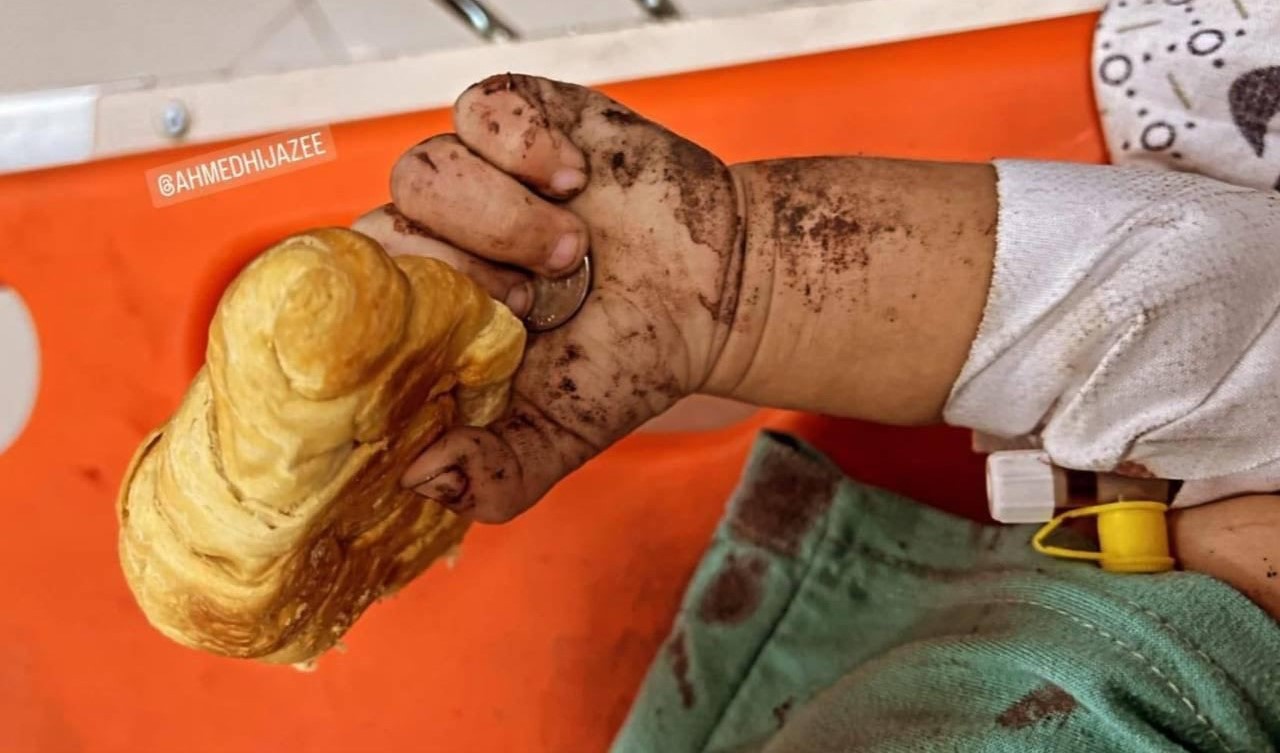
According to the World Health Organization, over half a million Palestinians are now living under confirmed famine conditions. Malnutrition has become a silent killer, claiming the lives of more than 360 Palestinians, including 130 children. The Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) places Gaza in Phase 5, which is the highest possible level of hunger emergency, categorized as Catastrophic. Gaza’s farms, bakeries, and water networks have been systematically destroyed, leaving families with little more than contaminated water and animal feed to survive.
The famine is not a natural consequence of war but a lethal weapon. Amnesty International has repeatedly stated that Israel is using starvation as a method of warfare, an act that meets the legal threshold for genocide.As per a report of Amnesty International published in October,
“Israel’s deliberate starvation of civilians is a war crime.”
Each blockade, each denied aid truck, and now each seized ship deepens this crime against humanity.
What is the Global Sumud Flotilla?
The flotilla, meaning steadfastness in Arabic, embodied the principle of Sumud, which means unshakable resistance. It consisted of more than 40 vessels and 500 international participants from 37 countries. Departing from ports across Europe and North Africa, it aimed to reach Gaza’s coast peacefully and symbolically challenge Israel’s naval siege. Among those on board were parliamentarians, humanitarian doctors, and activists, including climate advocate Greta Thunberg, united under one flag: human conscience.
Their mission was not to wage war, but to deliver aid and visibility. Yet as their ships neared Gaza, Israeli drones shadowed them, communications were jammed, and warning messages filled the airwaves. Finally came the interception.
The Interception: How the Siege Struck at Sea
Around midnight, Israeli commandos surrounded the final ship, Marinette, approximately 42.5 nautical miles off Gaza’s shore. Activists reported being forced to kneel for hours, zip-tied and beaten, as soldiers confiscated cameras and personal belongings. All contact was cut as the ships were redirected to Ashdod Port inside Israel. The Israeli military justified the action by claiming the flotilla violated a lawful blockade and that “no humanitarian aid was found aboard,” which is a statement disputed by multiple international witnesses.
More than 450 activists were detained, among them citizens of Spain, Italy, Turkey, South Africa, and the United States. Many were held without immediate consular access, with reports of inhumane treatment emerging within days. Amnesty International condemned the detentions as “an unlawful act of aggression” and a “deliberate effort to enforce collective punishment through starvation.”
Before communications were cut, Irish activist Tadhg Hickey recorded a final message: “We sail not just for Gaza’s survival, but for our own humanity. If silence is complicity, then to sail is resistance.” His words have since circulated across social media, embodying the flotilla’s spirit of nonviolent defiance.
Survivors deported to Turkey later described their ordeal. “We were treated like criminals for carrying food,” one volunteer said. “They zip-tied our wrists until they bled, but we’d do it again because Gaza is worth every risk.” Their testimonies echo the voices of thousands protesting globally after the interception, from London to Kuala Lumpur, demanding accountability and an end to the siege.
Law, Morality, and the Machinery of Blockade
The Israeli blockade, in place since 2007, has been condemned as illegal under international humanitarian law. The Fourth Geneva Convention forbids the collective punishment of civilians, and maritime law recognizes the right to deliver humanitarian aid in the face of mass suffering. Yet Israel continues to act with impunity, supported by global silence and diplomatic paralysis.
The United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) has warned that the blockade constitutes “a form of apartheid and starvation-based warfare.” Meanwhile, the UNRWA reports that 80% of Gaza’s population now depends on humanitarian aid for survival—aid that often never arrives.
Each intercepted vessel, carries a moral weight beyond its cargo. The Global Sumud Flotilla is more than a convoy; it was a reminder that humanity refuses to abandon Gaza to darkness. To criminalize compassion is to declare war on conscience itself.
Global Reactions and Outrage
Governments across the world have expressed alarm. Switzerland, Spain, and South Africa lodged formal protests, demanding explanations for the detention of their citizens. Turkish authorities arranged emergency flights to repatriate deported activists. Protests erupted in Paris, Istanbul, and Jakarta, as demonstrators carried placards reading, “Feeding Gaza is not a crime.”
Yet, in the corridors of power, condemnation remains cautious. Western governments have largely avoided direct criticism, framing the interception as a “security matter.” Meanwhile, humanitarian organizations, from Amnesty International to Human Rights Watch, have demanded that the blockade be lifted immediately and that the international community recognize the ongoing genocide.
The Broader Picture: Gaza’s Siege as Global Failure
The interception of the flotilla is not an isolated act, but the symptom of a global collapse of moral responsibility. While Gaza’s hospitals run without anesthesia and its children starve in makeshift tents, world leaders debate terminology instead of stopping the crime. Every intercepted aid convoy, every silenced activist, marks another day when humanity looked away.
The sea that once connected civilizations now separates the starving from salvation. Israel’s naval blockade is not a shield but a weapon. It starves, isolates, and erases. And yet, every time someone dares to sail toward Gaza, the truth resurfaces: even in the face of warships, the human spirit remains unsinkable.
However, the Global Sumud Flotilla did not fail, but it exposed the blockade for what it truly is: an act of cruelty sustained by silence. It reminded the world that solidarity still sails, that compassion still defies orders, and that Gaza’s struggle is humanity’s test.
Every intercepted ship tells the same story: that courage is contagious, that empathy is rebellion, and that the people of Gaza are not forgotten. The world may build walls of steel and propaganda, but the sea remembers those who dared to cross it—for justice, for life, and for Gaza.

 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago
 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured4 years ago
Featured4 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago
 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years ago
 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago