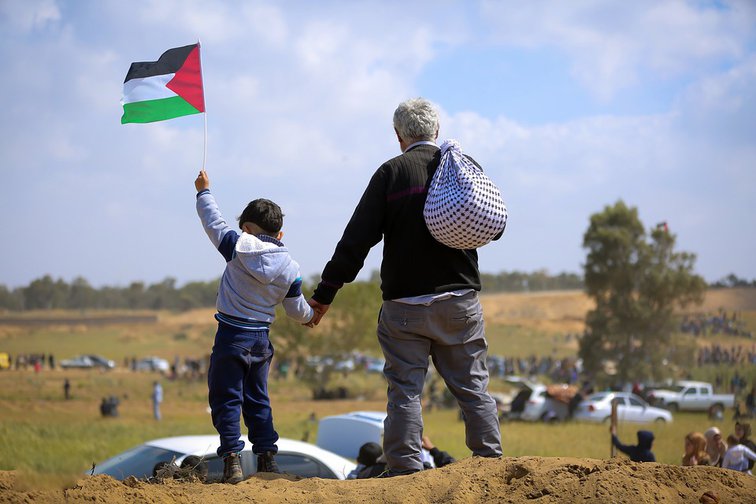
For the first time in months, the skies above Gaza seem quiet. No sirens, no distant thud of bombs, and no children running for shelter. This is a fragile silence – one that carries the weight of grief, exhaustion, and the faintest breath of hope. The newly brokered ceasefire between Israel and Hamas has brought an uneasy calm to a land battered beyond recognition. However, what does this truce really mean for Gaza, for its resilient people, and for the uncertain future that still lies ahead?
The Ceasefire Agreement: What is Promised?
Mediated by Egypt, Qatar, and the United States, the ceasefire agreement demands an immediate halt to military operations from both sides. Israeli troops have begun a phased withdrawal from central Gaza, while Hamas is set to release hostages in exchange for Palestinian detainees. Humanitarian aid, fuel, food, and medicines are promised unrestricted access through UN-coordinated corridors.
Yet, as with every truce before, skepticism lingers. The language of peace often hides the reality of fragility. Many Gazans call it not an end, but a pause, like a window to bury the dead and search for the living.
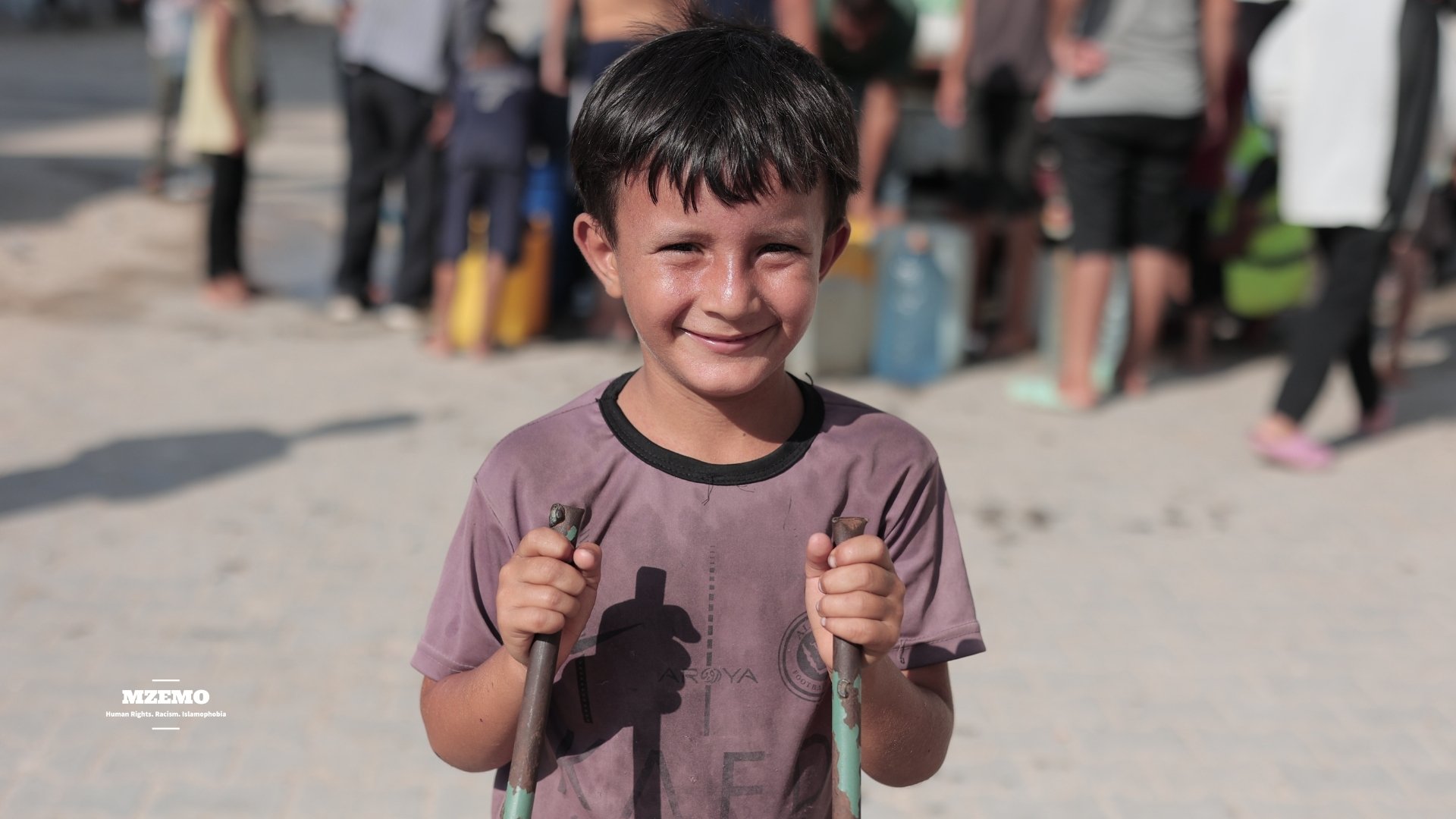
As the dust settles, Gaza reveals its new geography of loss. Satellite images show entire neighborhoods flattened. Hospitals that once stood as shelters now stand as ruins. Roads are cratered, schools turned into makeshift morgues. However, amid the destruction, thousands of displaced families are returning to what remains of their homes.
“We will rebuild even if it’s only with our hands,” says a father from Khan Younis, sweeping rubble from his doorway.
His words echo the quiet defiance of a people who have learned to survive without certainty.
Life Between the Lines of a Truce
Ceasefires in Gaza are rarely moments of celebration. They are interludes between wars and the days when families breathe, mend, and count who is still alive. Markets reopen with candlelight, children chase kites through streets of dust, and teachers gather students in the shells of classrooms.
Yet, the fear never truly leaves. Every drone hum is a reminder. Every tremor of glass recalls nights when silence meant danger. For many Gazans, peace feels less like a right and more like a borrowed hour.
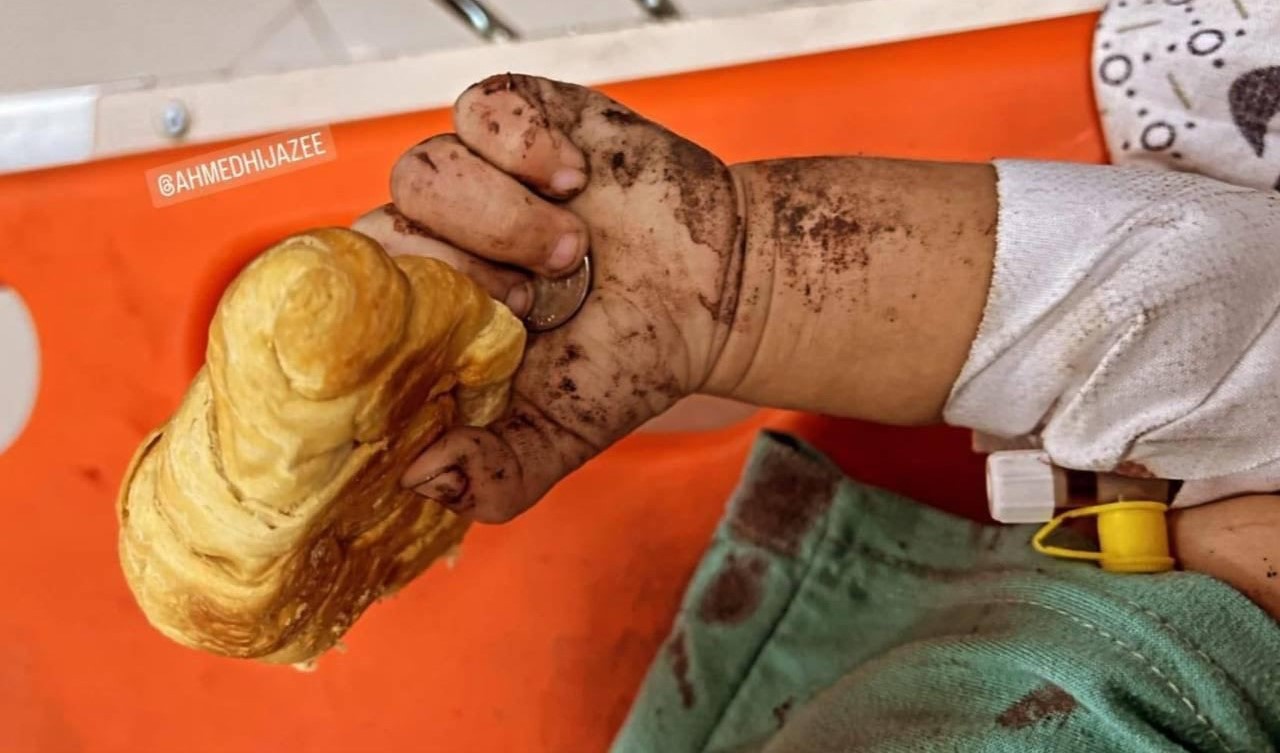
The ceasefire’s greatest test lies in the flow of aid. The United Nations and the Red Crescent have mobilized convoys to deliver supplies, yet logistical chaos and damaged roads make access painfully slow. Hospitals are desperate for anesthesia, blood bags, and clean water, while fuel shortages have forced surgeons to rely on battery lamps and hand-pumped oxygen.
UN officials warn that Gaza is at risk of famine. Every truck that enters carries not just food, but the hope of survival. However, the question still persists—will aid continue once the world’s attention shifts again?
Aid in the Balance: Lifelines Under Pressure
The true test of this ceasefire lies in how quickly and how fully aid flows. The United Nations plans a 60-day escalation in humanitarian deliveries. The goal is to assist 2.1 million people, provide nutrition support to 500,000, and deliver cash assistance to 200,000 families.
Even so, the UN warns that only 28% of the needed $4 billion appeal for Gaza has been funded. UNICEF, in a recent warning, said child mortality could spike if full food aid crossings were not allowed. Therefore, it is estimated that 50,000 children are at immediate risk of acute malnutrition.
Yet logistical barriers remain with wrecked roads, checkpoints, bureaucratic delays, and fuel shortages.
As one UN relief coordinator cautioned:
“This problem won’t go away in two months.”
Politics Behind the Pause
The ceasefire is not only humanitarian but also deeply political. For Israel, it provides breathing space amid growing international criticism. For Hamas, it offers a chance to claim survival as victory. For mediators like Egypt and Qatar, it is a test of diplomatic endurance.
However, beneath these maneuvers lies a truth that without accountability and justice, every ceasefire is temporary. History has seen these pauses crumble under mistrust, missteps, and the politics of vengeance.
Reconstruction promises are once again flooding global headlines. Nations pledge millions, NGOs draft blueprints, and donors speak of hope. But Gazans remember the promises of 2014 and 2021 when funds vanished, and aid projects never began.
This time, the call from Gaza is clear: let rebuilding belong to those who have lived through the ruins. Let aid be about dignity, not dependency.
The Global Conscience
As the truce holds, protests continue in cities from London to Jakarta. Millions march for justice, waving Palestinian flags, chanting for freedom and accountability. The ceasefire may have paused the bombs, but it has amplified Gaza’s voice.
International pressure is mounting for independent investigations into alleged war crimes. Human rights organizations warn that impunity will only plant the seeds of another conflict. The world is watching, but watching alone is not enough.
The fragility of peace in Gaza lies in its repetition as history is written in ceasefires that failed. Still, there is something different this time that a sense that Gaza’s agony has pierced the world’s conscience in a way that can no longer be ignored.
In the heart of the ruins, Gazans are not asking for sympathy. They are asking for justice, protection, and the right to live without counting the seconds between sirens.
Conclusion: Between Hope and History
The Gaza ceasefire is not an end to war but a fragile silence held together by the will of a broken people. It is a pause between grief and survival, between what was destroyed and what might still be rebuilt. Whether it becomes the beginning of peace or just another chapter of waiting depends not only on leaders or treaties, but on the world’s willingness to remember.
For now, Gaza breathes—quietly, painfully, defiantly.
“They have silenced our skies, but not our spirit.”

 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago
 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured4 years ago
Featured4 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago
 Featured5 years ago
Featured5 years ago
 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago
 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago